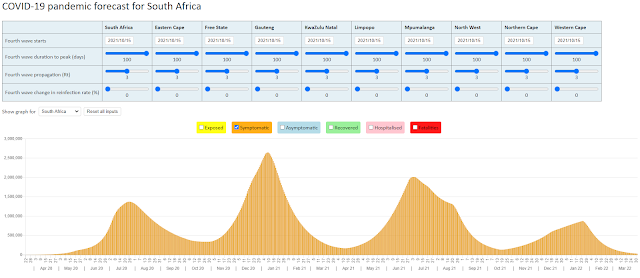
Herd immunity will be reached sooner than we thought
The logic of the SEIR epistemological models assumes that the virus will move through a population where all individuals are equally susceptible to infection. In practice the virus will be constrained in its movements by the social contact networks that exist in the population. The virus will infect the highly connected individuals first, and then the viral propagation will slow down when less connected individuals are left in the susceptible population.
This slowing down of the viral propagation has now been built into the NMG model so as not to overstate the numbers that are forecast to eventually become infected. A herd immunity parameter must be entered that represents the percentage of the population that is infected when the virus stops spreading in the population (when the reproduction number is below 1.00). The model transmission rate parameter is reduced in stages until this herd immunity parameter is attained to reflect this slowing down of the viral propagation.
A herd immunity parameter of 30% has been used as the default in the NMG model based on historical experience with past influenza pandemics (most notably the 1918 and 1957 pandemics) where around 30% of the population seem to have become infected. This has reduced the total COVID-19 deaths forecast by the NMG to model to just over 60 000 which is within the range of 48 300 and 88 000 given by the four scenarios in the Actuarial Society model.
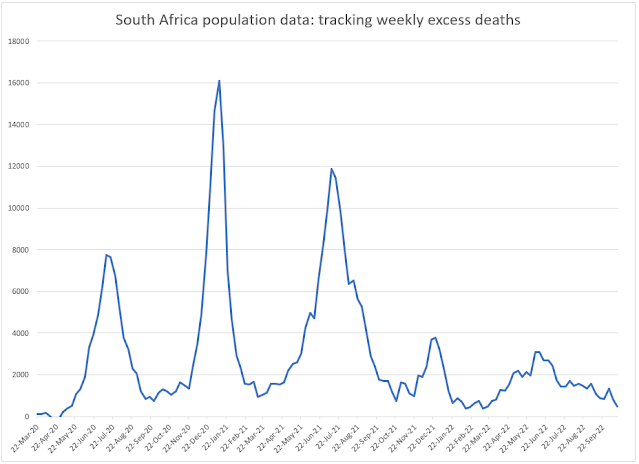
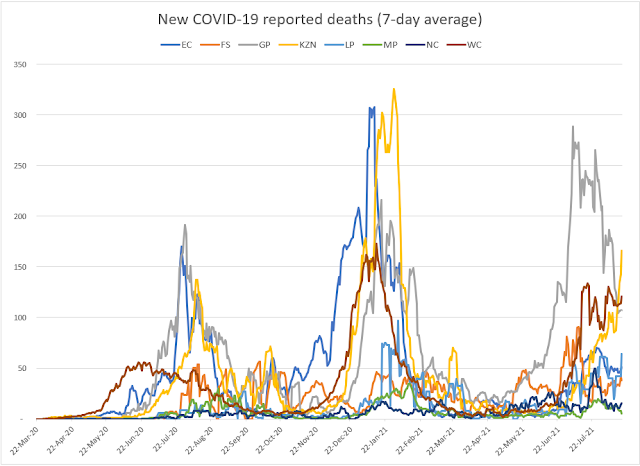
A comparison of this forecast for COVID-19 deaths and all-causes deaths is given below:
The all-causes deaths in 2020 continue to track below the numbers in 2019 due to the lockdown constraints in South Africa. The peak in COVID-19 deaths is expected to arrive in August. Let's hope that our hospitals will be ready to treat these patients.
12 May 2020


Comments
Post a Comment